Welcome, students! Navigating the world of academic and business studies can sometimes feel like learning a new language.
Terms like “TOWS analysis” might sound a bit daunting at first, but once you understand their meaning and how they apply in real-world scenarios, you’ll see how powerful these tools can be in shaping your thinking and decision-making.
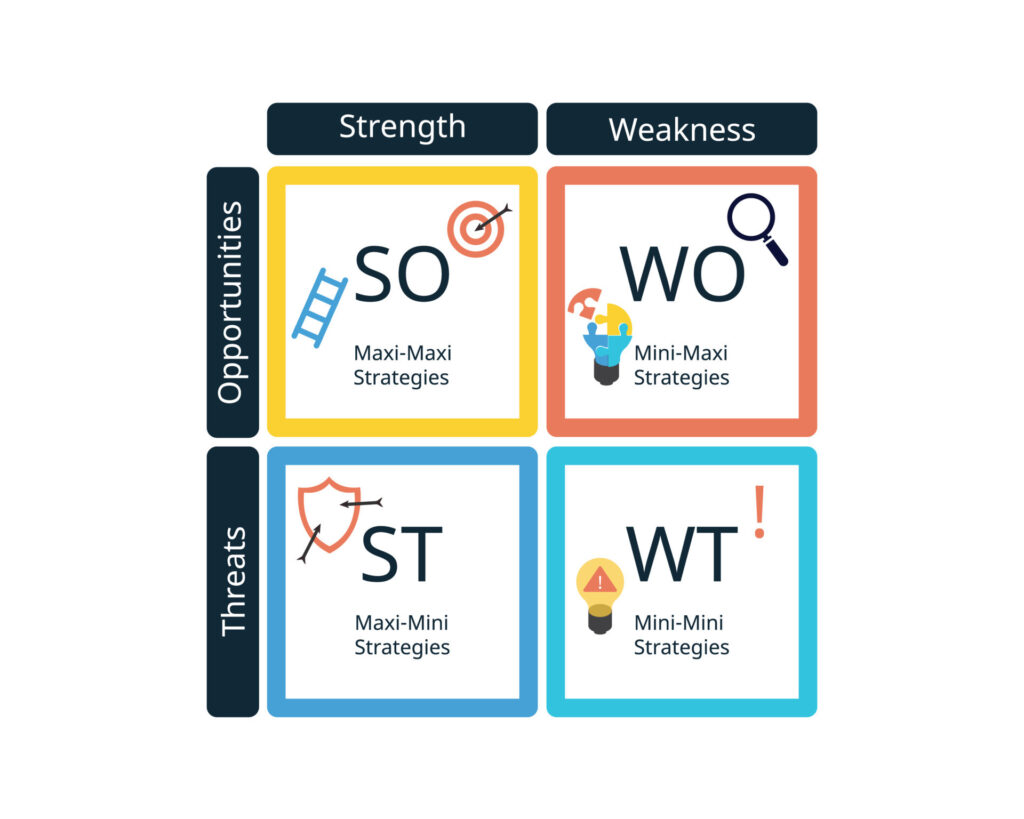
In today’s post, we’re going to demystify the TOWS analysis—a strategic planning method that’s not just theoretical but has real-world impact in the business landscape.
Let’s explore how some of the biggest companies use TOWS analysis to stay ahead of the curve, and by the end, you’ll be ready to apply these insights to your own studies and beyond.
Apple Inc. (Technology Industry)
Strengths (S): Strong brand reputation, loyal customer base, innovative product design.
Weaknesses (W): High prices, dependency on iPhone sales, limited customization options.
Opportunities (O): Expanding into emerging markets, increasing demand for wearable tech, growth in service-based revenue.
Threats (T): Intense competition from Android devices, supply chain disruptions, rapid technological changes.
TOWS Strategies:
SO (Maxi-Maxi): Apple can leverage its strong brand and loyal customer base to introduce innovative wearable products in emerging markets.
For instance, the Apple Watch can be marketed as an essential health tool in regions where wearable tech is just beginning to gain traction. By emphasizing health benefits and integrating with local health services, Apple can attract a new demographic that values both luxury and practicality.
WO (Mini-Maxi): To address the high prices that limit Apple’s reach in emerging markets, the company could develop more affordable versions of its key products, like an iPhone SE targeted at budget-conscious consumers.
Alongside this, Apple can expand its services like iCloud, Apple Music, and Apple Pay in these regions to build a recurring revenue stream that compensates for lower hardware margins.
ST (Maxi-Mini): Apple should use its strong brand to stay ahead of competitors by focusing on privacy and security—features that Android devices may struggle to match. For example, Apple could launch marketing campaigns that highlight its commitment to user privacy, positioning itself as the go-to brand for consumers concerned about data security.
WT (Mini-Mini): To reduce its dependency on iPhone sales, Apple could invest heavily in R&D for emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and autonomous vehicles. By doing so, Apple can diversify its product offerings and mitigate the risks associated with the slowing smartphone market.
Starbucks (Food and Beverage Industry)
Strengths (S): Strong global brand, extensive store network, premium product positioning.
Weaknesses (W): High operational costs, limited menu diversity in some regions, dependency on the US market.
Opportunities (O): Expansion into emerging markets, growth of the premium coffee segment, increasing demand for sustainable practices.
Threats (T): Economic downturns, competition from local coffee shops, volatility in coffee bean prices.
TOWS Strategies:
SO (Maxi-Maxi): Starbucks can capitalize on its global brand to expand into emerging markets, where the premium coffee experience is still developing. By tailoring its store designs and product offerings to local tastes—like introducing region-specific flavors—Starbucks can appeal to new customers while maintaining its premium image.
For example, in Asia, Starbucks has successfully introduced green tea-flavored beverages to align with regional preferences.
WO (Mini-Maxi): To reduce its dependency on the US market and diversify its revenue streams, Starbucks could focus on increasing its menu diversity in international markets. This can be achieved by introducing locally relevant food items or collaborating with local brands to create unique offerings.
For instance, Starbucks could partner with local bakeries in France to offer exclusive pastries that resonate with the local culture.
ST (Maxi-Mini): To maintain its premium positioning during economic downturns, Starbucks could strengthen its loyalty program, offering discounts or perks that keep customers engaged even when discretionary spending decreases.
Additionally, the company could emphasize its commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainability to differentiate itself from competitors, appealing to the growing segment of socially conscious consumers.
WT (Mini-Mini): Starbucks could streamline its operations to reduce costs and mitigate the impact of volatile coffee bean prices. This could involve investing in technology to improve supply chain efficiency, such as predictive analytics to better manage inventory and reduce waste.
Additionally, Starbucks could explore direct trade agreements with coffee growers to stabilize pricing and ensure a consistent supply of high-quality beans.
Tesla (Automotive Industry)
Strengths (S): Innovative technology, strong brand, first-mover advantage in electric vehicles (EVs).
Weaknesses (W): High production costs, limited production capacity, dependency on Elon Musk’s leadership.
Opportunities (O): Growing global demand for EVs, government incentives for green technology, advancements in battery technology.
Threats (T): Increasing competition in the EV market, supply chain issues, fluctuating raw material prices.
TOWS Strategies:
SO (Maxi-Maxi): Tesla can leverage its brand and technological innovation to dominate the growing global EV market.
For example, by expanding production facilities in regions with strong government incentives for green technology—such as Europe and China—Tesla can increase market share and capitalize on favorable policies. Tesla could also continue to innovate with features like full self-driving (FSD) technology, maintaining its position as a leader in the EV space.
WO (Mini-Maxi): To overcome production limitations and reduce costs, Tesla could invest in automated manufacturing processes and new battery technologies. For instance, Tesla’s Gigafactories, which focus on high-volume production of batteries and vehicles, are a direct response to the need to scale efficiently.
Additionally, partnerships with local suppliers can help Tesla minimize supply chain disruptions and reduce dependency on international shipping.
ST (Maxi-Mini): Tesla should continue to differentiate itself from emerging competitors by emphasizing its unique selling points, such as its extensive Supercharger network and over-the-air software updates.
By offering features that competitors cannot easily replicate, Tesla can retain its loyal customer base and attract new buyers who value cutting-edge technology.
WT (Mini-Mini): Tesla could mitigate the risks associated with fluctuating raw material prices by investing in alternative materials and recycling programs.
For example, Tesla’s efforts to develop in-house battery recycling facilities can help reduce reliance on volatile markets for raw materials like lithium, ensuring a more stable supply chain and cost structure.
Nike (Sportswear Industry)
Strengths (S): Strong global brand, extensive distribution network, high-quality product innovation.
Weaknesses (W): Dependency on third-party manufacturers, controversies around labor practices, reliance on key products.
Opportunities (O): Expansion in emerging markets, increasing health consciousness, growth in e-commerce.
Threats (T): Intense competition, fluctuating material costs, potential regulatory changes on labor practices.
TOWS Strategies:
SO (Maxi-Maxi): Nike can leverage its global brand and innovative product lines to tap into the growing demand for sportswear in emerging markets.
For instance, Nike could introduce affordable, region-specific products that cater to local sports or cultural preferences, while promoting its brand’s association with top athletes and sports teams.
WO (Mini-Maxi): To address its reliance on third-party manufacturers, Nike could invest in more sustainable and transparent supply chain practices.
This could involve creating vertically integrated manufacturing facilities or developing partnerships with manufacturers that adhere to strict labor and environmental standards. By doing so, Nike can improve its brand image and reduce risks associated with labor controversies.
ST (Maxi-Mini): To stay ahead of competitors, Nike should continue to innovate in both product design and marketing. For example, Nike’s use of advanced materials like Flyknit technology not only sets it apart from competitors but also addresses consumer demand for lightweight and sustainable products.
Additionally, Nike can use digital platforms to engage directly with consumers, offering personalized shopping experiences through apps and social media.
WT (Mini-Mini): Nike could mitigate the impact of fluctuating material costs by investing in alternative materials and sustainable sourcing practices.
For example, Nike’s “Move to Zero” campaign, which focuses on reducing carbon emissions and waste, aligns with this strategy by promoting the use of recycled materials and more efficient manufacturing processes.
These examples of TOWS analysis show how companies can strategically align their strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats. By doing so, they can develop actionable strategies that not only address current challenges but also position them for future success.
Whether you’re a student or a business professional, understanding how to apply TOWS analysis in real-world scenarios is a valuable skill that can help you navigate complex environments and make informed decisions.
Conclusion
 And there you have it—TOWS analysis in action! By understanding how companies like Apple, Starbucks, Tesla, and Nike strategically align their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can see the practical value of these academic concepts.
And there you have it—TOWS analysis in action! By understanding how companies like Apple, Starbucks, Tesla, and Nike strategically align their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can see the practical value of these academic concepts.
As you continue your journey in school and later in your career, remember that these tools aren’t just for big corporations; they’re for anyone who wants to make informed, strategic decisions.
Whether you’re working on a group project, preparing a business plan, or just trying to understand the world around you, the TOWS analysis is a powerful ally.
Keep practicing, stay curious, and you’ll find that these concepts will soon become second nature. Happy studying!
0 Comments
Leave a reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.




